This section covers the following syllabus (Physics 5059) requirements.
show understanding that all physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
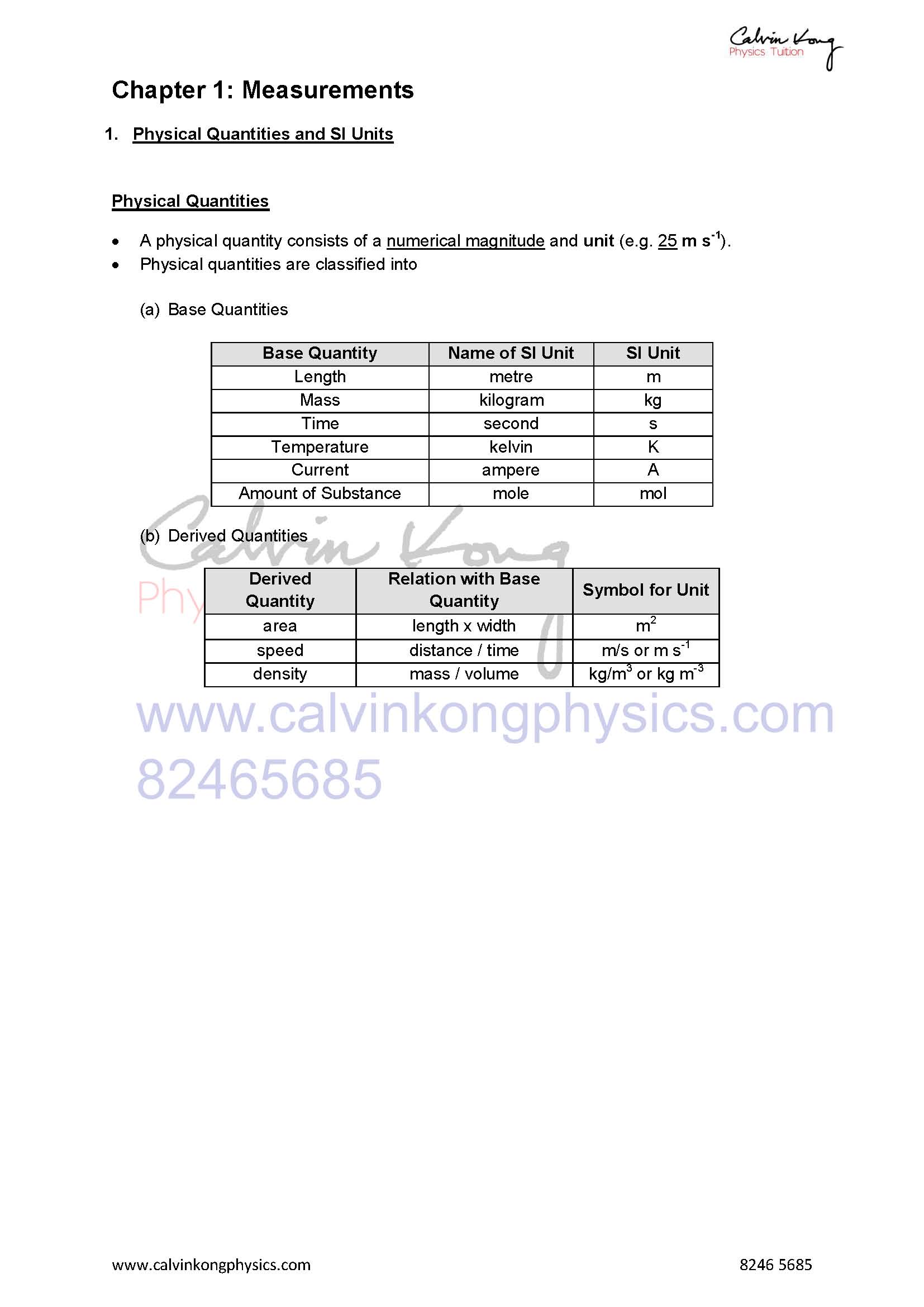
recall the following base quantities and their units: mass (kg), length (m), time (s), current (A), temperature (K), amount of substance (mol)
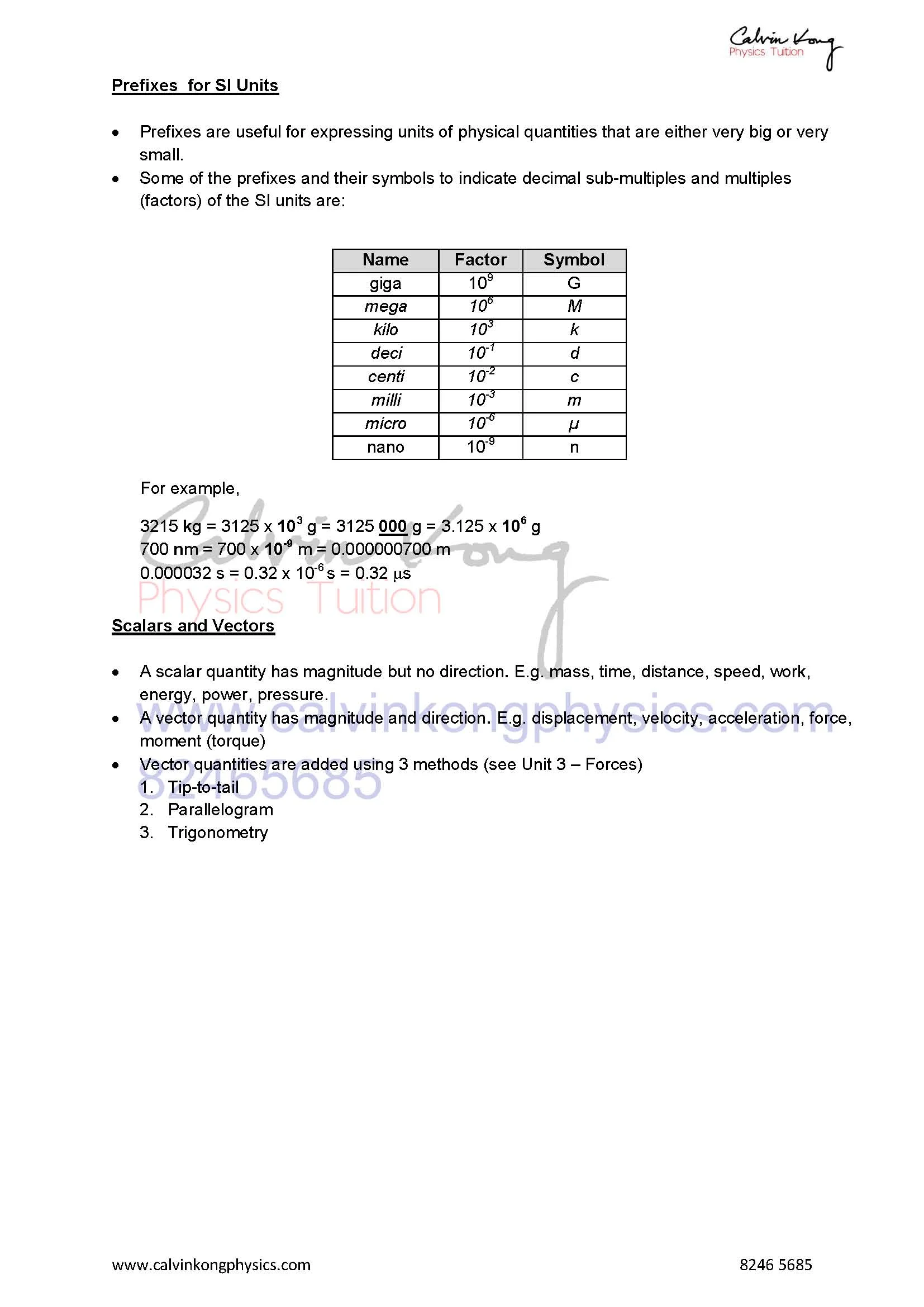
use the following prefixes and their symbols to indicate decimal sub-multiples and multiples of the SI units: nano (n), micro (μ), milli (m), centi (c), deci (d), kilo (k), mega (M), giga(G)
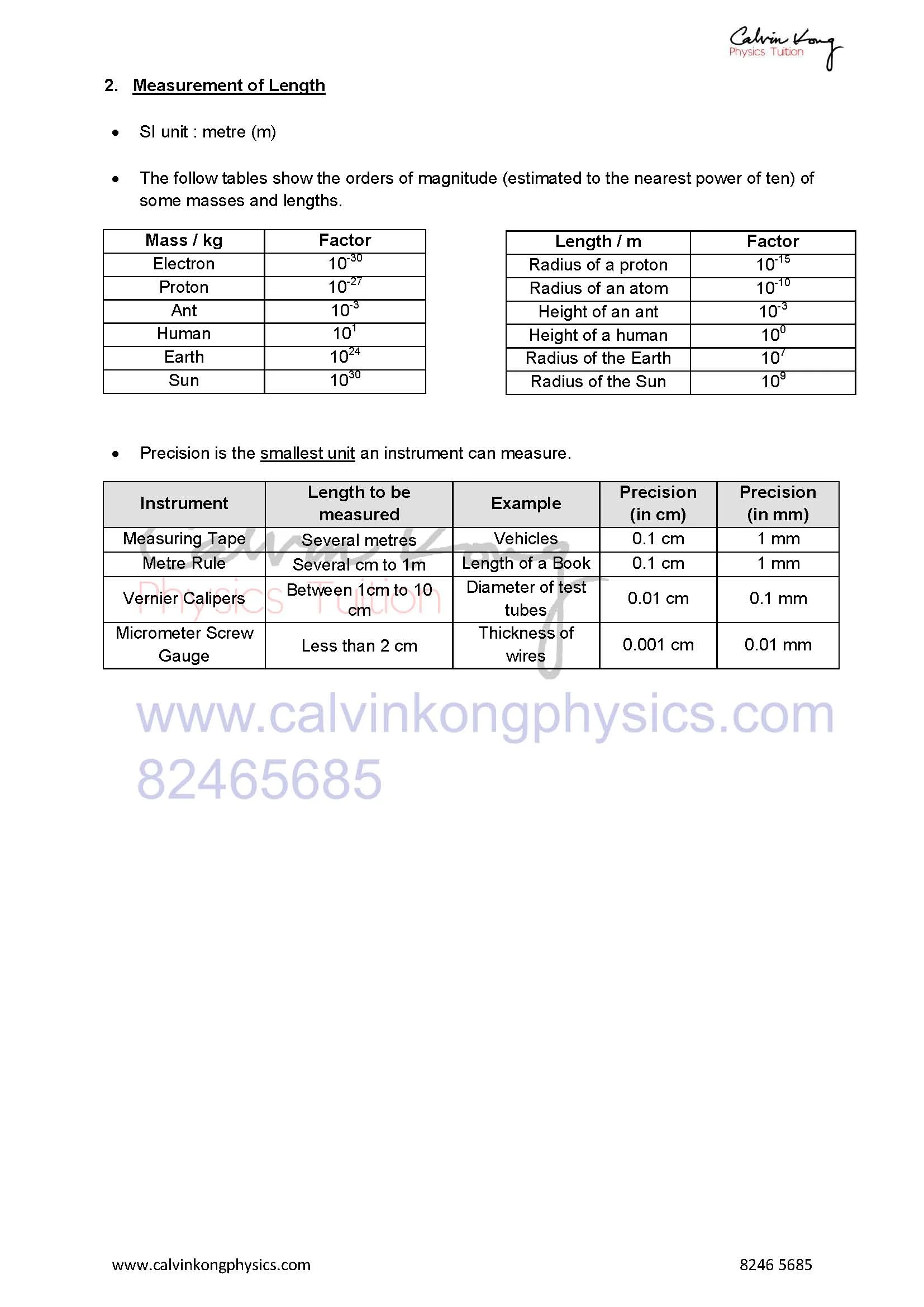
show an understanding of the orders of magnitude of the sizes of common objects ranging from a typical atom to the Earth
state what is meant by scalar and vector quantities and give common examples of each